Groupe Allergie, infection respiratoire et immunité
Publications principales
2025
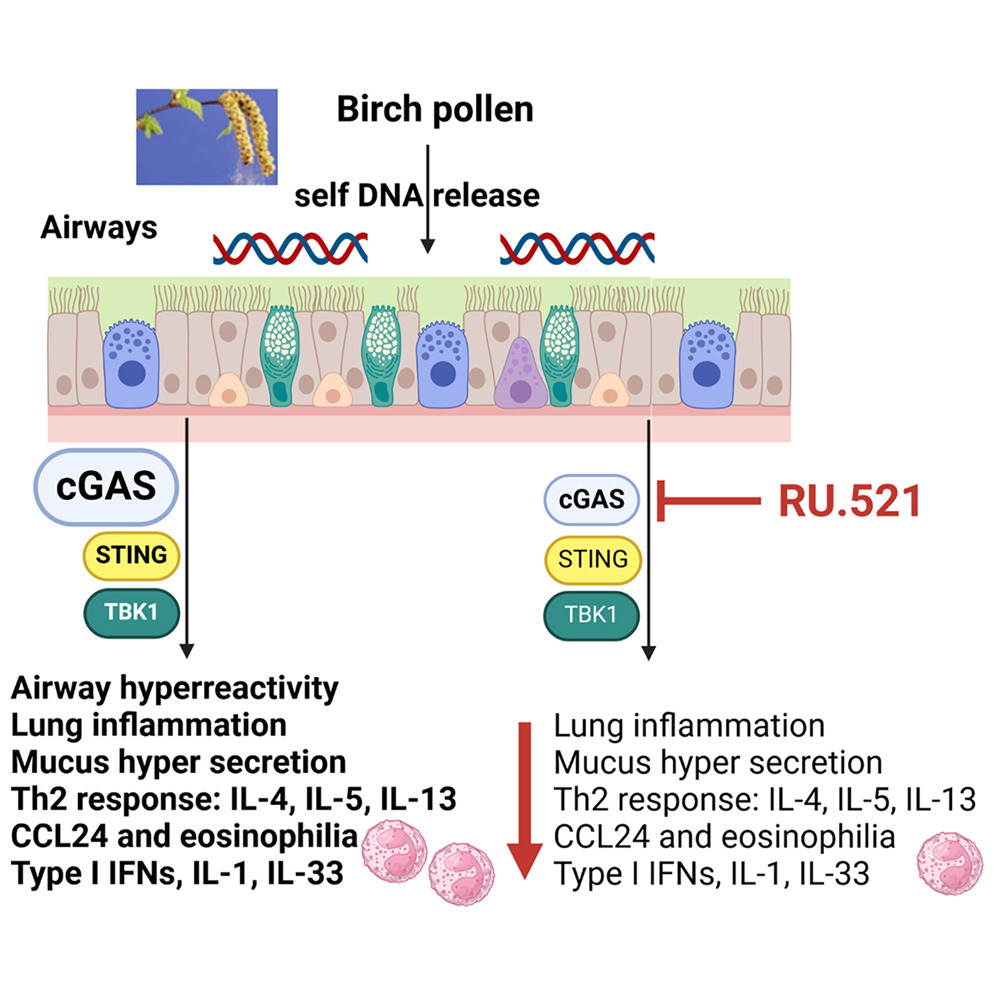
Allergens trigger airway dsDNA release and DNA sensor cGAS-STING expression
Allergen-induced dsDNA release correlates with type 2 cytokines in the airways
Reduced allergen-type 2 immune response in cGAS- or STING-deficient mice
cGAS inhibitor protects from allergen airway inflammation and type 2 response
cGAS-STING DNA-sensing in inflammatory bowel diseases.
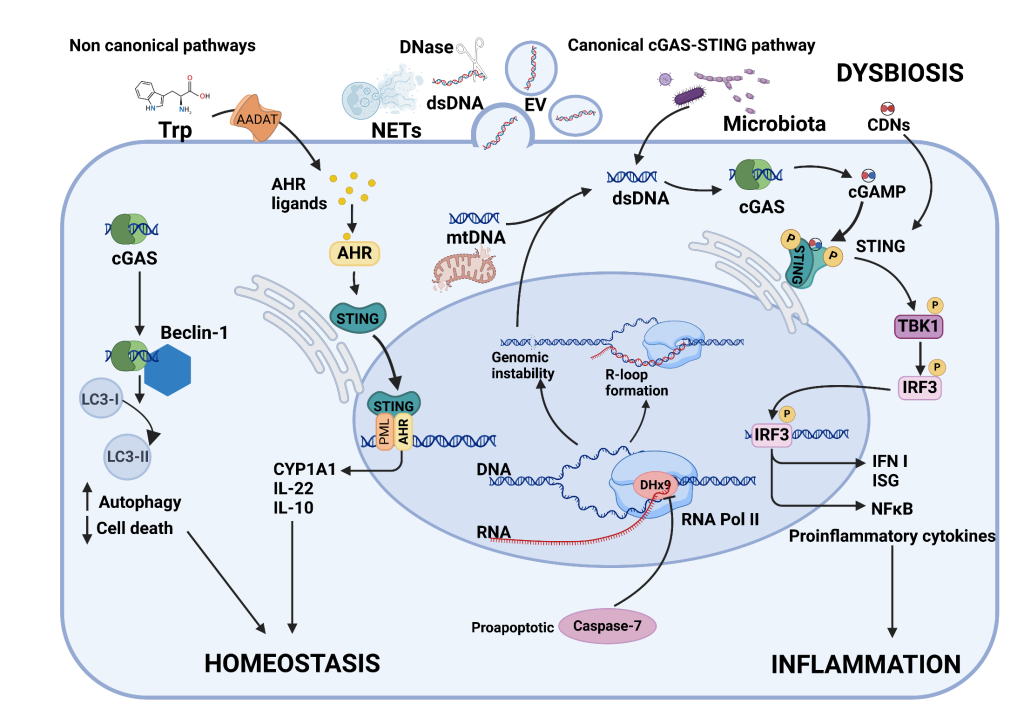
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), ulcerative colitis (UC), and Crohn’s disease (CD) are chronic, incurable pathologies with unknown causes, affecting millions of people.
Intestinal lesions in IBD are due to infiltrates of activated immune cells in gut wall with secretion of proinflammatory cytokines. Intestinal mucosal damage and cell death with ectopic DNA release may activate the DNA-sensing cGAS-STING pathway. Increased colonic cGAS and STING are reported in human UC and CD, with cell-free DNA of nuclear and mitochondrial origin, correlating to clinical and histological status in UC. Murine colitis models show cGAS and STING activation and type I interferon response. Interference in the cGAS-STING pathway may alleviate experimental colitis.
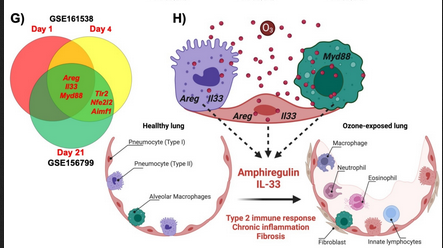
The current data suggest that O3-induced oxidative stress is a central event-inducing oxeiptotic cell death pathway. O3-induced epithelial barrier damage and cell death, trigger the release of alarmins and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), with subsequent endogenous activation of Toll-like receptors (TLRs), DNA sensing pathways, and inflammasomes, activating IL-1-Myd88 inflammatory pathway with the production of a range of chemokines and cytokines. This cascade orchestrates lung tissue-resident cell activation in response to O3 in leukocyte and non-leukocyte populations, driving sterile innate immune response. Chronic inflammatory response to O3, by repeated exposures, supports a mixed phenotype combining asthma and emphysema, in which their exacerbation by other particulate pollutants potentially culminates in respiratory failure.
STING-dependent induction of neutrophilic asthma exacerbation in response to house dust mite.
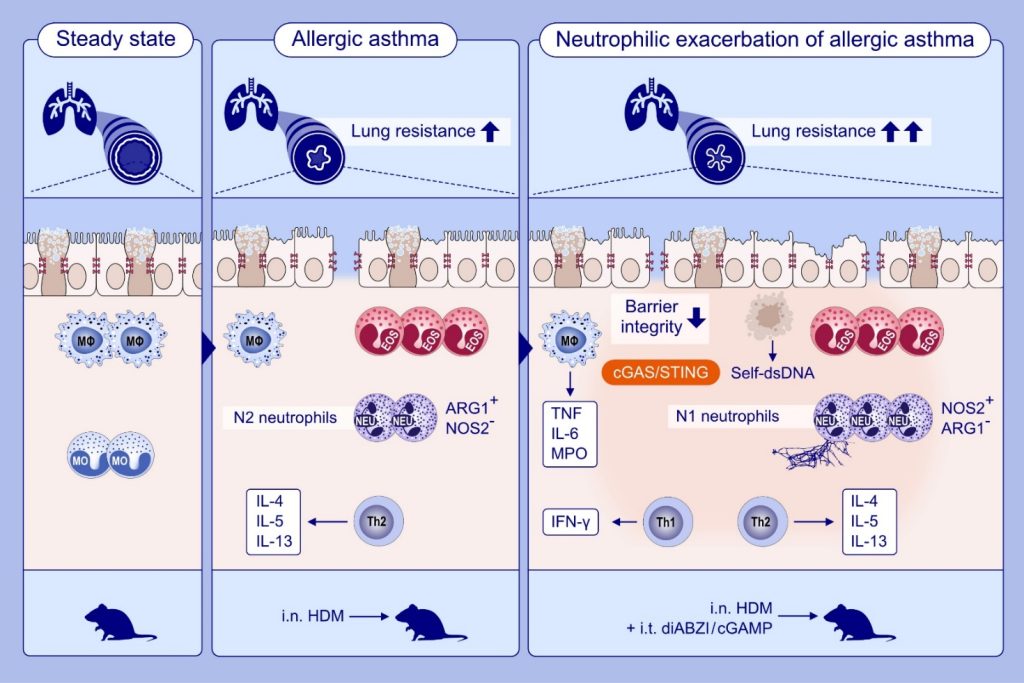
This study investigates whether STING-induced neutrophilic lung inflammation mimics severe asthma. STING activation during allergic challenge triggers neutrophilic asthma accompanied by a Th1 and pro-inflammatory cytokine in addition to the Th2 cytokines resulting in an epithelial barrier damage, cell death and self-dsDNA release with increased mucus hypersecretion. STING agonists induce N2 (ARG1+NOS2-) versus N1 (NOS2+ARG1-) neutrophil polarization and NETs formation.
2022
Synthesis of novel 3’,3’-cyclic dinucleotide analogues targeting STING protein
Magand J, Roy V, Meudal H, Rose S, Quesniaux V, Chalupska D, Agrofoglio LA. Asian J Organic Chem 2022, e202200597 doi: .org/10.1002/ajoc.202200597 - hal-03859427, v1
Synthesis of novel 3’,3’-cyclic dinucleotide analogues targeting STING protein
Magand J, Roy V, Meudal H, Rose S, Quesniaux V, Chalupska D, Agrofoglio LA. Asian J Organic Chem 2022, e202200597 doi: .org/10.1002/ajoc.202200597 - hal-03859427, v1
2021
Chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa Lung Infection Is IL-1R Independent, but Relies on MyD88 Signaling.
MMP-9 Mediates Cross-Talk between Neutrophils and Endothelial Cells in Psoriasis.Alves-Filho JC, Marcel Silva Melo B, Ryffel B.
Innate type 1 immune response, but not IL-17 cells control tuberculosis infection. Segueni N, Jacobs M, Ryffel B.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

